Gear oil is used to lubricate manual transmissions and differentials, while differential oil specifically lubricates differentials. Both oils serve crucial functions in ensuring smooth vehicle operation and reducing friction between gears and components.
Gear oil is designed to handle the high pressures and temperatures within manual transmissions, while differential oil is formulated to withstand the unique demands of differentials. Understanding the differences between gear oil and differential oil is essential for maintaining optimal performance and prolonging the lifespan of your vehicle’s drivetrain components.
Let’s delve deeper into the distinctions between these two types of lubricants and their specific roles in vehicle maintenance.
Gear Oil Versus Differential Oil: The Basics
Gear oil and differential oil serve distinct purposes: gear oil lubricates manual transmissions and transaxles, while differential oil lubricates the differential. Gear oil handles the gears’ sliding action, while differential oil allows the ring and pinion gears to rotate smoothly.
The main difference lies in their specific functions within the vehicle’s drivetrain.
Key Properties Of Gear Oil
Gear oil and differential oil are two types of lubricants that play crucial roles in the smooth operation of a vehicle’s transmission system. While they are often used interchangeably, it’s important to understand the key properties that differentiate gear oil from differential oil. Gear oil is specifically formulated to provide lubrication and protection to the gears within the transmission system. It possesses several key properties that make it suitable for this purpose. First and foremost, gear oil has a high viscosity, which means it is thick and resistant to flow. This viscosity helps to cushion and separate the gear teeth, reducing friction and wear. Additionally, gear oil has excellent thermal stability, allowing it to withstand the high temperatures generated by the gears during operation. This helps to prevent the oil from breaking down and losing its lubricating properties. Another important property of gear oil is its extreme pressure (EP) additives. These additives ensure that the oil can handle the immense pressure and shock loads that occur between the gear teeth. They form a protective layer on the gear surfaces, preventing metal-to-metal contact and reducing the risk of damage.Essential Functions Of Differential Oil
Differential oil, on the other hand, serves a different purpose within the vehicle’s transmission system. The differential is responsible for distributing power evenly between the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds. Differential oil is designed to lubricate and cool the gears and bearings within the differential assembly. One of the key functions of differential oil is to provide proper lubrication to the differential gears. These gears are subject to high speeds and heavy loads, so the oil needs to have the right viscosity to ensure smooth operation and reduce wear. Additionally, differential oil helps to dissipate heat generated by the gears, preventing overheating and potential damage. Another crucial function of differential oil is to protect the differential gears and bearings from corrosion and rust. Differential assemblies are often exposed to harsh conditions, such as water, dirt, and debris. The oil forms a protective barrier, preventing these contaminants from causing damage and extending the lifespan of the differential components. In conclusion, while both gear oil and differential oil are essential for the proper functioning of a vehicle’s transmission system, they have distinct properties and functions. Gear oil is formulated to provide lubrication and protection to the gears, while differential oil focuses on lubricating and cooling the differential assembly. Understanding these differences can help ensure that the right type of oil is used for each specific application, promoting optimal performance and longevity.Viscosity And Additives: Tailoring For Performance
Viscosity and additives play crucial roles in tailoring the performance of gear oil and differential oil. Understanding the differences in their viscosity and the impact of additives is essential for optimizing the performance and longevity of your vehicle’s drivetrain components.
The Role Of Viscosity In Lubrication
Viscosity determines the oil’s resistance to flow, affecting its ability to lubricate moving parts effectively. In gear oil, higher viscosity is required to withstand the extreme pressure and sliding motion between gears. In contrast, differential oil needs lower viscosity to ensure smooth operation and minimize power loss within the differential mechanism.
Additives And Their Impact On Oil Performance
Additives are incorporated into gear and differential oils to enhance their performance characteristics. Anti-wear additives form a protective layer on metal surfaces, while extreme pressure additives prevent metal-to-metal contact under high loads. Additionally, friction modifiers are used in differential oil to reduce friction and improve fuel efficiency, whereas rust and corrosion inhibitors protect metal surfaces from degradation.
Types Of Gear Oil: Varieties And Uses
Mineral Vs Synthetic Gear Oils
Mineral gear oils are derived from refined crude oil and are suitable for standard driving conditions. They provide adequate lubrication and heat resistance for everyday use. On the other hand, synthetic gear oils are chemically engineered for superior performance. They offer better lubrication, improved thermal stability, and enhanced wear protection, making them ideal for high-stress applications.
Specialized Gear Oils For Extreme Conditions
For extreme operating conditions, specialized gear oils are available to meet specific requirements. These include limited-slip differential oils for vehicles equipped with limited-slip differentials, as well as hypoid gear oils designed for hypoid gears commonly found in rear axles. These specialized oils provide tailored protection to ensure optimal performance and durability under demanding circumstances.
Differential Oil Explained: Composition And Characteristics
Gear oil and differential oil are both used in automobiles, but they serve different purposes. Gear oil is used in manual transmissions, while differential oil is used in the differential. Differential oil has a different viscosity and composition than gear oil, making it better suited for the differential’s unique needs.
Standard Differential Oil Formulations
Differential oil is a lubricant that is used in the differential of a vehicle to reduce friction and wear. It is specifically designed to withstand the high pressures and temperatures that are generated by the gears. There are several standard differential oil formulations available in the market, each with its unique characteristics and composition. The most commonly used differential oil is mineral-based, which is a combination of base oil and additives. Synthetic-based differential oil is also available, which is made up of synthetic base oil and advanced additives. These formulations offer higher performance and longer service life compared to mineral-based oils.The Importance Of Friction Modifiers
Friction modifiers are essential additives that are added to differential oil to improve its performance. They help to reduce friction between the gears, resulting in smoother operation and reduced wear and tear. The use of friction modifiers is especially important in limited-slip differentials, which require a specific level of friction to operate correctly. When selecting differential oil, it is crucial to choose a product that contains the correct amount and type of friction modifiers to ensure optimal performance. Overall, differential oil is a vital component in the proper functioning of a vehicle’s differential. It is essential to choose the right oil formulation and ensure that it contains the right additives to achieve the best performance and longevity. By understanding the composition and characteristics of differential oil, you can make an informed decision and keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.Application Specifics: When To Use Each Oil
Manual transmissions need gear oil for lubrication.
Use oil with the correct viscosity and additives.
Differentials require differential oil for smooth operation.
Use oil specifically formulated for differentials.

Credit: www.e38.org
The Impact Of Wrong Oil Usage
Incorrect usage of oil can have a significant impact. Understanding the difference between gear oil and differential oil is crucial for proper maintenance and performance of your vehicle. Gear oil is used in manual transmissions and differentials, while differential oil is specifically designed for differentials to provide lubrication and heat dissipation.
Using the wrong oil can lead to increased wear, reduced efficiency, and potential damage to your vehicle’s components. Ensure you use the correct oil to avoid costly repairs and ensure optimal performance.
Consequences For The Gear System
Using the wrong oil in a gear system can have severe consequences. The gear system relies on proper lubrication to reduce friction and wear between the gears. When the wrong oil is used, it can lead to increased friction and heat, causing the gears to wear out faster. This can result in noisy operation, reduced efficiency, and ultimately, the failure of the gear system.Risks To The Differential Mechanism
The differential mechanism is a crucial component of a vehicle’s drivetrain, responsible for distributing power between the wheels. When incorrect oil is used in the differential, it can lead to various risks. One significant risk is increased friction, which can cause excessive heat buildup and eventually lead to the failure of the differential. Additionally, using the wrong oil can result in poor lubrication, leading to increased wear and tear on the differential’s components. This can result in a loss of traction, reduced vehicle control, and potentially costly repairs. Using the correct oil for both the gear system and the differential is essential to ensure their smooth operation, longevity, and overall performance of the vehicle. It is important to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or seek professional advice to determine the appropriate oil specifications for your specific gear system and differential. Taking this precautionary step can help you avoid the detrimental consequences and risks associated with the use of incorrect oil.Maintenance Tips: Ensuring Optimal Performance
To ensure optimal performance, understanding the difference between gear oil and differential oil is crucial. Gear oil is designed for manual transmissions, while differential oil is specifically formulated for rear-wheel drive differentials. Using the right oil for each component will help maintain the efficiency and longevity of your vehicle.
Regular Oil Checks And Changes
Regular oil checks and changes are essential to maintain optimal performance of your vehicle. Gear oil and differential oil play crucial roles in ensuring the smooth operation of your car’s transmission and differential system. Therefore, it’s vital to check the oil levels and change the oil at regular intervals to keep your vehicle running smoothly.Detecting Signs Of Oil Degradation
Detecting signs of oil degradation is also important to ensure your vehicle’s optimal performance. Over time, oil can break down, become contaminated, and lose its lubricating properties. This can cause excessive wear and tear on your vehicle’s transmission and differential system, resulting in poor performance and costly repairs. Therefore, it’s important to be aware of signs of oil degradation, such as strange noises, difficulty shifting gears, and leaks, and to take action immediately if you notice any of these signs.Proper Oil Selection
Proper oil selection is also important to ensure your vehicle’s optimal performance. Not all oils are created equal, and using the wrong type of oil can cause serious damage to your vehicle’s transmission and differential system. Therefore, it’s important to use the recommended oil type and viscosity as specified in your vehicle’s owner manual.Professional Maintenance
Finally, professional maintenance is also crucial to ensure your vehicle’s optimal performance. Regular maintenance, such as oil changes and inspections, should be performed by a qualified mechanic to ensure that your vehicle is in top condition. A professional mechanic can also diagnose and repair any issues with your vehicle’s transmission and differential system before they become major problems. In conclusion, regular oil checks and changes, detecting signs of oil degradation, proper oil selection, and professional maintenance are all essential to ensure your vehicle’s optimal performance. By following these maintenance tips, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and avoid costly repairs in the future.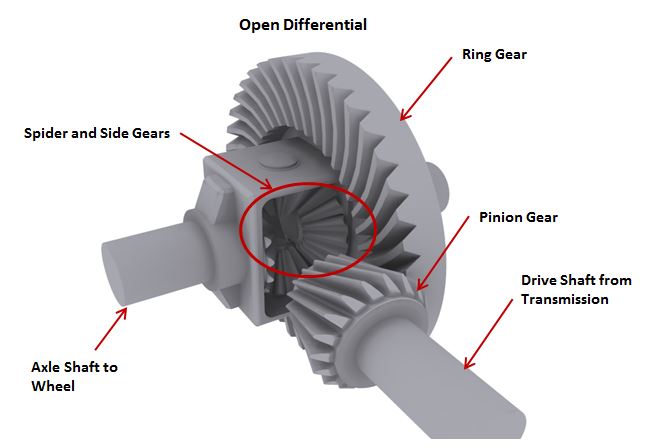
Credit: blog.amsoil.com
Expert Insights: Mechanic’s Advice On Oil Selection
Professional Recommendations
When it comes to gear oil and differential oil, mechanics emphasize choosing the right type based on your vehicle’s needs.
For gear oil, experts suggest using high-quality lubricants with the correct viscosity to ensure smooth gear operation.
When it comes to differential oil, mechanics recommend selecting oils specifically designed for differentials to prevent wear and tear.
Common Myths Debunked
- Myth: Gear oil and differential oil are interchangeable. – Fact: Each serves a unique purpose.
- Myth: Using any oil will work fine. – Fact: Choosing the right oil is crucial for optimal performance.
- Myth: All gear oils are the same. – Fact: Variations exist based on viscosity and additives.
Credit: blog.amsoil.com
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between gear oil and differential oil is crucial for proper vehicle maintenance. Gear oil is used in manual transmissions and differentials, while differential oil is specifically designed for differentials. Using the right oil for each component ensures optimal performance and longevity for your vehicle’s drivetrain.
Always consult your vehicle’s manual for the recommended oil types and change intervals.


