Engine oil is designed for lubricating internal combustion engines, while gear oil is for transmissions and differentials. Both oils have specific viscosities and additives tailored to their respective functions.
Engine oil protects against wear and heat in engines, while gear oil provides lubrication and protects against high pressure and shock loads in gearboxes. Understanding the difference between these oils is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of automotive components.
Let’s delve deeper into the distinctions between engine oil and gear oil to make informed decisions when it comes to lubricating our vehicles.
Introduction To Engine And Gear Oil
When it comes to the smooth operation of a vehicle, the type and quality of lubricants used play a crucial role. Engine oil and gear oil are two essential types of lubricants that ensure the proper functioning of the engine and transmission system, respectively. Understanding the differences between these two types of oil is vital for maintaining the performance and longevity of a vehicle.
The Role Of Lubricants In Vehicles
Lubricants are substances that reduce friction and wear between moving parts, ensuring smooth operation and preventing damage. In vehicles, lubricants play a critical role in minimizing heat and friction in various components, thereby enhancing overall efficiency and performance. Engine and gear oils are specifically formulated to meet the unique lubrication requirements of engines and transmissions.
Primary Functions Of Engine And Gear Oil
- Lubrication: Engine oil forms a protective layer between moving parts, reducing friction and wear.
- Cooling: It helps in dissipating heat generated during the combustion process, preventing overheating.
- Cleaning: Engine oil removes contaminants and deposits, keeping the internal components clean and free from sludge buildup.
- Lubrication: Gear oil reduces friction and wear in the transmission system, ensuring smooth gear shifting and operation.
- Protection: It safeguards gears and bearings from damage, extending the lifespan of transmission components.
- Viscosity: Gear oil maintains the required viscosity for proper lubrication under varying operating conditions.

Credit: shieldoils.com
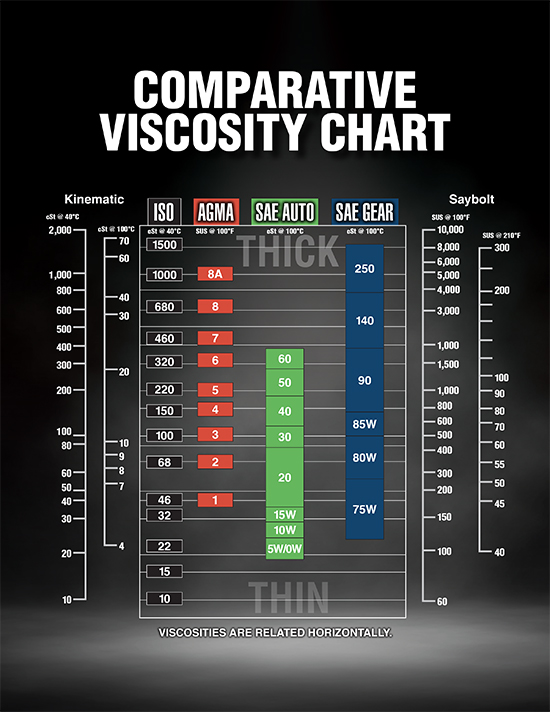
Viscosity Grades Explained
Viscosity grades play a crucial role in understanding the differences between engine oil and gear oil. It’s important to know how these grades impact the performance and protection of your vehicle’s engine and transmission. Let’s delve into the detailed explanation of viscosity grades and their impact.
Understanding Viscosity Ratings
Viscosity ratings, represented by numbers and letters, indicate the oil’s flow characteristics at different temperatures. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) developed a standardized system to classify viscosity grades. For instance, a multi-grade oil like 10W-30 demonstrates its flow at both cold (10W) and hot (30) temperatures. Higher numbers denote thicker oils and lower numbers signify thinner oils.
Impact On Performance And Protection
The viscosity rating directly influences the oil’s ability to lubricate engine components and provide necessary protection. In engines, the right viscosity ensures proper lubrication at startup and consistent protection during high-temperature operation. Similarly, gear oil with appropriate viscosity safeguards transmission components from wear and tear, maintaining optimal performance and longevity.
Chemical Composition Contrast
Engine oil and gear oil differ significantly in their chemical compositions.
Base Oils And Additives
Engine oil primarily contains base oils and additives.
Base oils in engine oil are refined from crude oil.
Additives enhance engine oil’s properties like lubrication and viscosity.
Unique Formulations For Different Applications
Gear oil, on the other hand, has distinct formulations for specific applications.
It contains extreme pressure additives for gear protection.
Viscosity modifiers ensure gear oil performs under high pressure.
Temperature Tolerance
Engine oil and gear oil have different temperature tolerances. Engine oil is designed to withstand high temperatures generated by the engine, while gear oil is formulated to handle the extreme pressures and temperatures within the transmission and differential. Understanding these temperature tolerances is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of your vehicle’s engine and transmission system.
High Heat Resistance
When it comes to temperature tolerance, engine oil and gear oil have different properties. Engine oil is designed to withstand high temperatures, typically up to 250°F, without breaking down. Gear oil, on the other hand, is formulated to handle even higher temperatures, often up to 300°F or more. This is because the gears in a transmission can generate a lot of heat due to friction, and gear oil needs to be able to withstand this heat to keep the transmission running smoothly.Cold Weather Performance
While gear oil is better suited for high temperatures, engine oil is better suited for cold temperatures. Engine oil flows more easily in cold weather than gear oil, which can become thicker and more viscous. This can make it difficult for the gears to turn, leading to increased wear and tear on the transmission. Engine oil, on the other hand, remains fluid even in cold temperatures, allowing it to flow smoothly through the engine and lubricate the moving parts. In conclusion, when it comes to temperature tolerance, engine oil and gear oil have different properties. Engine oil is better suited for high temperatures, while gear oil is better suited for cold temperatures. So, it’s important to choose the right oil for your vehicle based on the conditions you’ll be driving in. By doing so, you can ensure that your engine and transmission are properly lubricated and running smoothly for years to come.Wear And Tear Protection
When it comes to the maintenance of your vehicle’s engine and gearbox, wear and tear protection is of utmost importance. The right choice of lubricants, such as engine oil and gear oil, can significantly impact the longevity and performance of these vital components.
Anti-wear Additives In Engine Oil
Engine oil is specifically formulated to provide lubrication and protection to the internal components of an engine. One crucial aspect of engine oil is the presence of anti-wear additives, which are designed to minimize friction and prevent metal-to-metal contact.
These additives create a protective film on the engine’s moving parts, such as the pistons, camshaft, and bearings. The film acts as a barrier, reducing wear and tear caused by the high-stress conditions within the engine.
The anti-wear additives work by forming chemical bonds with the metal surfaces, reducing friction and preventing excessive wear. This not only extends the life of the engine but also enhances its overall performance.
Extreme Pressure Additives In Gear Oil
Gear oil, on the other hand, is specifically designed for the gearbox and other mechanical components that transmit power within the vehicle. Gearboxes operate under high pressures and extreme conditions, which necessitates the use of specialized lubricants.
One key component in gear oil is the presence of extreme pressure additives. These additives are responsible for protecting the gears from wear and tear caused by the immense pressure and sliding contact between the gear teeth.
Extreme pressure additives form a protective layer on the gear surfaces, reducing friction and preventing metal-to-metal contact. This layer withstands the high pressures and ensures smooth gear operation, minimizing wear and extending the gearbox’s lifespan.
In addition to wear and tear protection, gear oil also provides cooling and heat dissipation properties to handle the increased temperatures generated by the gearbox during operation.
| Anti-Wear Additives in Engine Oil | Extreme Pressure Additives in Gear Oil |
|---|---|
| Minimize friction and metal-to-metal contact | Protect gears from wear under high pressure |
| Create a protective film on engine parts | Form a protective layer on gear surfaces |
| Extend engine life and enhance performance | Ensure smooth gear operation and longevity |
Choosing the right lubricants for your engine and gearbox is essential for ensuring optimal wear and tear protection. Engine oil with anti-wear additives safeguards your engine’s internal components, while gear oil with extreme pressure additives protects the gears from excessive wear.
Regularly checking and changing these lubricants as per the manufacturer’s recommendations is crucial for maintaining the performance and longevity of your vehicle’s engine and gearbox.
Credit: blog.amsoil.com
Oil Change Intervals
Regular oil changes are vital for the longevity and smooth functioning of any vehicle. Engine oil and gear oil are two of the most commonly used lubricants in vehicles. While engine oil lubricates the engine’s internal parts, gear oil is used to lubricate the transmission and differential parts.
Recommended Service Life For Engine Oil
The recommended service life for engine oil varies depending on several factors, including the type of oil used, driving conditions, and the make and model of the vehicle. Generally, it is recommended to change the engine oil every 5,000 to 7,500 miles for conventional oil and every 10,000 to 15,000 miles for synthetic oil.
However, it is always best to refer to the vehicle owner’s manual for the manufacturer’s recommended service life for engine oil. Manufacturers often recommend shorter oil change intervals for vehicles that are driven in harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures or dusty environments.
Gear Oil Durability And Change Frequency
Gear oil is designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it more durable than engine oil. However, like engine oil, the durability of gear oil depends on several factors, including the type of oil used, driving conditions, and the make and model of the vehicle.
Generally, it is recommended to change the gear oil every 50,000 to 100,000 miles. However, if the vehicle is driven in harsh conditions, such as towing heavy loads or driving in extreme temperatures, it may be necessary to change the gear oil more frequently.
Regular oil changes are essential for maintaining the health of your vehicle’s internal parts. While the recommended service life for engine oil varies depending on several factors, it is generally recommended to change the engine oil every 5,000 to 7,500 miles for conventional oil and every 10,000 to 15,000 miles for synthetic oil. Gear oil is more durable than engine oil and is recommended to be changed every 50,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on driving conditions.
Compatibility With Vehicle Components
Compatibility with vehicle components is a crucial aspect to consider when choosing between engine oil and gear oil. While engine oil is designed to lubricate the engine components, gear oil is formulated to work with the transmission and differential components.
Therefore, it is important to select the right type of oil to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the vehicle.
Seal Materials And Oil Compatibility
Engine oil and gear oil must be compatible with the seal materials in the vehicle.
- Choose oils that match the seal materials to prevent leaks.
- Improper oil selection can cause degradation of seals.
Clutch And Transmission Interactions
The interaction between clutch and transmission is crucial for smooth operation.
- Using the wrong oil can lead to clutch slippage.
- Proper oil selection ensures optimal transmission performance.
Environmental And Economic Considerations
Considering environmental and economic aspects, choosing between engine oil and gear oil is crucial. Engine oil is more versatile, while gear oil is specialized for transmissions. Each has unique benefits and impacts on both performance and sustainability. Making an informed decision is key.
Disposal And Recycling Differences
Engine oil and gear oil have distinct disposal and recycling methods. – Engine Oil: Can be recycled into other products. – Gear Oil: Often requires specialized disposal services.Cost-benefit Analysis Of Oil Types
Comparing the economic aspects of engine oil and gear oil. – Engine oil is generally more cost-effective. – Gear oil tends to be pricier due to its specific properties.Choosing The Right Oil For Your Vehicle
When it comes to maintaining your vehicle, choosing the right oil is crucial. Engine oil and gear oil are the two main types of lubricants used in vehicles. While both are important, they serve different functions and using the wrong one can cause serious damage to your vehicle. In this article, we will discuss the differences between engine oil and gear oil and help you choose the right oil for your vehicle.
Manufacturer Recommendations
One of the most important factors to consider when choosing between engine oil and gear oil is the manufacturer’s recommendations. Your vehicle’s owner’s manual will provide you with the recommended type of oil for your engine and transmission. It is important to follow these recommendations to ensure that your vehicle performs optimally and to avoid any potential damage.
Performance And Longevity Considerations
Performance and longevity are also important factors to consider when choosing between engine oil and gear oil. Engine oil is designed to lubricate the moving parts of the engine and protect it from wear and tear. On the other hand, gear oil is designed to lubricate the gears and other moving parts of the transmission. Using the wrong oil can lead to poor performance and reduced longevity.
When choosing between engine oil and gear oil, it is important to consider the viscosity and additives. Viscosity refers to the oil’s resistance to flow. Thicker oils have a higher viscosity and are better suited for high-performance engines, while thinner oils are better suited for everyday driving. Additives are chemicals added to the oil to improve its performance. Some additives can improve fuel efficiency, while others can reduce wear and tear on the engine or transmission.
Ultimately, the decision between engine oil and gear oil comes down to your vehicle’s specific needs. By following the manufacturer’s recommendations and considering performance and longevity considerations, you can choose the right oil for your vehicle and ensure that it runs smoothly and reliably for years to come.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Faq 1: What Is The Difference Between Engine Oil And Gear Oil?
Engine oil is designed to lubricate and cool the engine, while gear oil is formulated to lubricate the gears in the transmission and differential. Engine oil is thinner and has additives to protect against high temperatures, whereas gear oil is thicker and has additives to withstand the high pressures and extreme conditions in the transmission.
Faq 2: Can I Use Engine Oil Instead Of Gear Oil?
No, it is not recommended to use engine oil instead of gear oil. Engine oil and gear oil have different formulations and properties, and using the wrong type of oil can lead to poor performance, increased wear, and potential damage to the transmission.
Always use the recommended type of oil specified by the manufacturer.
Faq 3: What Happens If I Put Gear Oil In The Engine?
Putting gear oil in the engine can cause serious damage. Gear oil is not designed to be burned and does not have the necessary additives to protect the engine. It can lead to increased friction, reduced lubrication, and potential engine failure.
If you accidentally put gear oil in the engine, it is important to drain and replace it with the correct type of oil as soon as possible.
Faq 4: How Often Should I Change Engine Oil And Gear Oil?
The frequency of oil changes depends on various factors such as driving conditions, vehicle type, and manufacturer recommendations. Generally, engine oil should be changed every 3,000 to 5,000 miles or every 3 to 6 months. Gear oil, on the other hand, typically requires less frequent changes, ranging from every 30,000 to 50,000 miles or every 2 to 3 years.
It is important to consult your vehicle’s owner manual for specific recommendations.
Conclusion
Choosing the right oil for your vehicle is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the differences between engine oil and gear oil is essential for proper maintenance. By considering the specific needs of your vehicle, you can make an informed decision that will benefit your engine and transmission in the long run.


