The primary types of oil pumps used in engines are gear, rotor, and vane pumps. Each system has its unique characteristics tailored to specific engine requirements.
Understanding the different types of oil pumps is crucial for maintaining engine health and performance. Oil pumps are the heart of an engine’s lubrication system, required to keep moving parts lubricated, reduce friction, and dissipate heat. Gear pumps, popular for their simplicity and durability, use meshing gears to pump oil.
Rotor pumps, also known as gerotor pumps, utilize an inner and an outer rotor for oil transportation and are praised for their efficiency and quiet operation. Lastly, vane pumps, which feature sliding vanes in a rotor, offer a variable displacement design, making them adaptable to different engine conditions. Selecting the appropriate oil pump is essential for ensuring reliability and longevity of any internal combustion engine.
Introduction To Engine Lubrication
An engine’s heartbeat relies on oil, a vital fluid ensuring smooth operation. Without proper lubrication, engines struggle, wear out quickly, and eventually fail. This system’s core is the oil pump, a crucial component that keeps everything running smoothly.
Importance Of Oil Pumps
Oil pumps form the foundation of engine health. These mechanical heartbeats circulate life-sustaining oil. A constant flow is crucial. Oil pumps reduce friction and prevent engine wear. Their failure spells disaster, leading to engine damage or total failure.
The various types of oil pumps cater to different engine designs:
- Gear pumps – common and reliable.
- Rotary pumps – compact and quiet.
- Gerotor pumps – efficient flow at low speeds.
Main Functions Of Engine Oil
Engine oil serves multiple purposes that are crucial for performance and longevity:
- Lubricates engine parts to reduce friction.
- Absorbs and disperses heat from the engine.
- Prevents corrosion by inhibiting rust formation.
- Keeps the engine clean by suspending dirt and debris.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Gear Pumps: A Traditional Choice
Within the heart of an engine lies the oil pump, a critical component for its health and longevity. Among the various types of oil pumps, gear pumps stand out as a traditional and widely used choice. They have been reliably circulating oil in engines for decades, ensuring parts move smoothly and wear is minimized. Let’s dive into the workings of gear pumps and weigh their benefits against their limitations.
Working Principle
The core mechanism of gear pumps is both elegant and efficient. Two interlocking gears rotate within a tightly fitted casing. As these gears spin, they create suction at the pump’s inlet. This action draws oil into the chamber. The meshing of the gears then pushes the oil through the outlet, providing a steady flow to the engine’s moving parts. This continuous process is essential for engine protection and effectiveness.
Advantages And Limitations
Gear pumps offer several advantages that have cemented their use in engines:
- Consistent oil flow regardless of engine speed
- Simple construction leads to durability and lower costs
- Easy maintenance due to fewer moving parts
However, they do come with some limitations:
- Less efficient at high speeds compared to other types
- Can be noisy, as the gear teeth engage and disengage
- Potential for wear over time due to gear friction
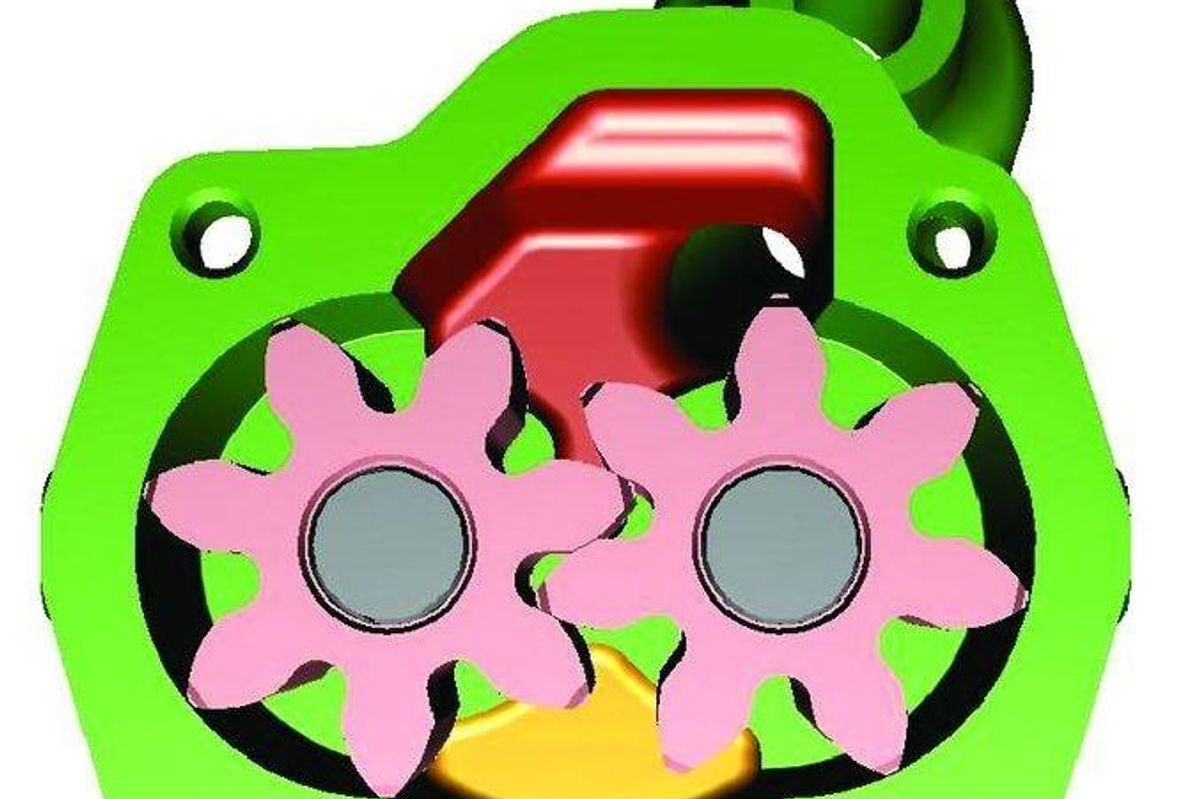
Rotor Pumps: The Inner Workings
The heart of an engine’s lubrication system is often a rotor pump, a key player in keeping everything running smoothly. Let’s dive into the inner workings of rotor pumps and see just how they contribute to an engine’s lifeblood.
Design And Operation
In the realm of rotor pumps, precision and efficiency are kings. These pumps consist of two rotors: an inner one, known as the rotor, and an outer one, called the annulus or stator. The key to their operation lies in the subtle twist of the rotors. They mesh together within a precisely machined pump housing.
- The rotor has lobes; the annulus has corresponding recesses.
- As the rotor turns, it traps oil between the lobes and the housing.
- This trapped oil moves around the outer edge and is pushed through the engine.
Imagine the rotor’s lobes as hands, gently scooping up the oil and guiding it on its path to vital engine parts. Simple, yet incredibly effective.
Benefits In Engine Performance
Rotor pumps shine when it comes to improving engine performance. Their design offers a continuous flow of oil, regardless of engine speed. This translates to a handful of perks for the engine:
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Consistency | Regular oil flow at all times |
| Reduced Wear | Less friction among parts |
| Lower Noise | Smooth operations are quieter |
| Enhanced Longevity | Healthy oil life extends engine life |
Every rotation of a rotor pump means a steady heartbeat for your engine, sustaining its performance and keeping those pistons pumping with joy!
Read More: Can Oil Pump Make Knocking Noise?
Vane Pumps: Precision And Adaptability
Vane pumps stand out in the realm of engine oil pumps. Thanks to their high precision and adaptability, they are a top choice for various applications.
Mechanism Of Vane Pumps
Inside a vane pump, a rotor spins with retractable vanes. These vanes spread out due to centrifugal force and hydraulic pressure. They maintain close contact with the pump’s inner walls. This creates chambers that transport oil.
- The rotor is off-center, making chamber sizes change as it turns.
- Oil is sucked in when chambers enlarge.
- When they shrink, oil is pushed out.
The beauty of this design lies in its constant flow, regardless of pressure.
Suitability For Modern Engines
Now, let’s explore why vane pumps are suited for today’s engines.
- They offer a smooth, pulsation-free oil flow.
- Vane pumps operate effectively over a broad range of temperatures and speeds.
- With their ability to adjust to engine demand, they are fuel-efficient.
- Reduced wear and tear is a plus, due to fewer moving parts.
- Their adaptability makes them perfect for complex engine designs seen in modern vehicles.
In summary, vane pumps provide a blend of precision and versatility, serving as an integral component in many engine configurations.
Plunger Pumps: High Pressure Solutions
Plunger pumps are vital in engines requiring high pressure, consistent lubrication. They turn the engine’s revolutions into hydraulic power. This helps the engine run smoothly. These pumps deliver pressurized oil to bearings and other crucial components.
Structure And Mechanism
At the heart of these pumps is a simple yet powerful design. A plunger pump consists of a cylinder, a plunger, and valves. Plungers move up and down inside the cylinder.
This action creates pressure that forces oil through the engine. The pump’s valves control the flow of oil. They ensure a steady supply even at high speeds.
Use In Specialized Applications
Plunger pumps are perfect for situations needing precise oil pressure. It is true for high-performance engines and industrial machinery.
- Racing cars use them for optimal performance.
- Heavy-duty equipment relies on these pumps for constant operation.
From construction sites to agricultural fields, plunger pumps keep engines going. They handle tough jobs with ease.

Credit: www.hemmings.com
Comparative Analysis Of Pump Types
Within an engine, the oil pump is the heart of the lubrication system. It ensures vital components stay lubricated. Different pumps have unique features. Let’s dive into how these pumps differ, focusing on efficiency, output, durability, and maintenance.
Efficiency And Output
Choosing the right oil pump is crucial for an engine’s performance. Efficiency refers to how well a pump converts power to flow. Output is the volume of oil it can move.
- Gear pumps are reliable. They offer steady flow rates.
- Rotary vane pumps adapt to pressure changes. They can maintain efficiency across different engine conditions.
- Gerotor pumps are compact. They fit in tighter engine spaces.
Durability And Maintenance
Long-lasting pumps save money and time. Choosing a pump with high durability means fewer replacements. Maintenance includes cleaning and part replacement.
| Type of Pump | Durability | Maintenance Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Gear Pumps | High | Low |
| Rotary Vane Pumps | Medium | Medium |
| Gerotor Pumps | Medium-High | Low-Medium |
Emerging Technologies In Oil Pumps
Engines need oil for smooth running. But not all engines work the same. They need different oil amounts at different times. Enter smart oil pumps. These new pumps adjust how much oil they pump. They do this to match what the engine needs. That saves energy. It means your car uses less fuel. It also cuts down on emissions. Now let’s look at two key techs changing oil pumps today.
Variable Displacement Pumps
Variable displacement pumps are smart. These pumps change their output. They match the engine’s oil need. When an engine is quiet, the pump works less. When the engine works hard, the pump works more. This tech helps cars save fuel and last longer. It’s becoming very popular in new engine designs.
Smart Pump Systems
Smart pump systems take it further. These systems use sensors and computers. They check the engine all the time. The pump adjusts in real-time. This gives the perfect oil flow. Smart systems also react to temperature changes. They keep the oil pressure just right. This is good for the engine and your pocket.
Here are the benefits these technologies bring to your car:
- Better fuel efficiency
- Reduced emissions
- Improved engine life
- Adapts to different driving styles
Choosing The Right Oil Pump
When diving under the hood of your vehicle, choosing the right oil pump is crucial. The oil pump is the heart of the engine’s lubrication system. It keeps everything running smoothly. Not all oil pumps are the same. Picking the perfect one matters for your engine’s lifespan and performance.
Factors To Consider
Selection involves a few key decisions.
- Engine Type: Know if you have a performance, standard, or heavy-duty engine.
- Pump Type: Gear, rotor, or vane? Each works differently.
- Size and Fit: Ensure compatibility with your engine’s dimensions and specs.
- Oil Viscosity: Thicker oils require stronger pumps.
- Brand Quality: Trustworthy brands often lead to fewer headaches down the road.
Impact On Engine Health
The oil pump’s impact on engine health is undeniable.
Poor Lubrication: Leads to increased friction and wear.
Overheating: Without the right oil flow, heat can’t escape, damaging engine parts.
Premature Engine Failure: A mismatched or failing pump can shorten engine life.
For these reasons, invest time in choosing a pump that ensures peak performance and longevity.
Installation And Maintenance
The proper installation and ongoing maintenance of oil pumps are key to engine performance. This section covers how to ensure your oil pump serves its purpose effectively.
Professional Installation Tips
Installing an oil pump demands precision. Follow these guidelines for success:
- Choose the correct pump type. Match it with your engine’s requirements.
- Gather all needed tools. This ensures a smooth installation process.
- Prepare the area. Clean and organize your workspace.
- Inspect parts before installation. Check for defects or damage.
- Follow manufacturer’s instructions. This will help avoid mistakes.
- Test for functionality. Always test the pump after installation.
Routine Maintenance Guide
Regular maintenance ensures longevity. Use this guide for routine oil pump upkeep:
- Check oil level frequently. Top up as needed.
- Monitor pressure gauges. Look for irregularities.
- Replace filters regularly. Dirty filters hinder performance.
- Inspect for leaks regularly. Address them promptly.
- Consult your manual for specifics. Each model has unique care instructions.
Schedule professional inspections bi-annually. Experts can spot issues early.
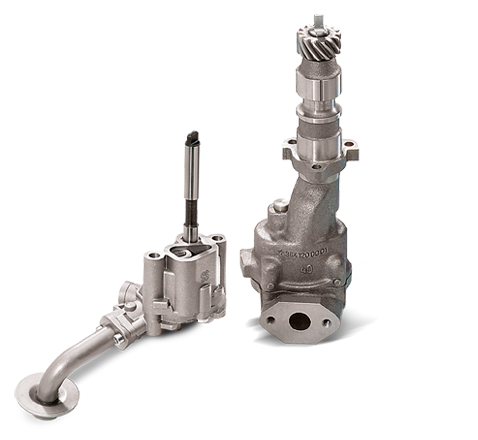
Credit: www.my-cardictionary.com
Future Of Engine Oil Pumps
As engines evolve, so do their components. The engine oil pump, critical for lubricating moving parts, faces transformations to meet modern demands. Featuring higher efficiency and integration with new engine technologies, the oil pump’s future shines with promise. Let’s delve into what innovation lies ahead for this essential engine component.
Innovation In Pump Design
Innovative designs are shaping the next generation of engine oil pumps. Engineers focus on creating pumps that offer variable flow rates to reduce energy consumption. These smart pumps adjust their output according to the engine’s needs. Additionally, new materials are in use to reduce weight and friction, further boosting efficiency.
Influence Of Electric Vehicles
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) brings significant changes to the auto industry. Traditional internal combustion engines (ICEs) and their oil pumps must adapt or face obsolescence. For hybrid vehicles, dual-purpose pumps that work with both ICEs and EV systems are in development. All-electric vehicles won’t have engine oil pumps, but they do require efficient cooling and lubrication solutions for gearboxes and other components, which paves the way for innovative fluid circulation systems.
- Variable flow rate technology
- Weight and friction reduction materials
- Dual-purpose pump designs
- Fluid circulation systems for EVs
Frequently Asked Questions On What Are The Different Types Of Oil Pumps Used In Engines?
What Are The Different Types Of Oil Pumps?
Oil pumps are categorized as gear, rotor, vane, and plunger types. Gear pumps use meshing gears, while rotor pumps employ interlocking screws. Vane pumps operate with sliding vanes, whereas plunger pumps use a reciprocating plunger. Each type suits different viscosity and pressure requirements.
What Are The Three Basic Types Of Engine Oil Pumps?
The three basic types of engine oil pumps are gear pumps, rotary vane pumps, and plunger pumps. Each type offers different advantages for various engine designs.
What Is The Most Commonly Used Oil Pump?
The most commonly used oil pump is the gear pump, widely favored for its simplicity and efficiency in circulating engine oil.
What Are The Three Types Of Oil Pumps Used In Automatic Transmissions?
The three types of oil pumps in automatic transmissions are gear, vane, and rotor pumps. Each ensures efficient fluid circulation within the system.
Read More: 5.3 Vortec Engine Oil Pump
Conclusion
Understanding the various oil pumps in engines is crucial for automotive maintenance. Whether it be a gear, rotor, or vane pump, each plays a pivotal role in engine health. By recognizing their differences and functions, you ensure optimal lubrication and performance.
Keep your engine running smoothly by choosing the right oil pump.


